Columns
| Column | Type | Size | Nulls | Auto | Default | Children | Parents | Comments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
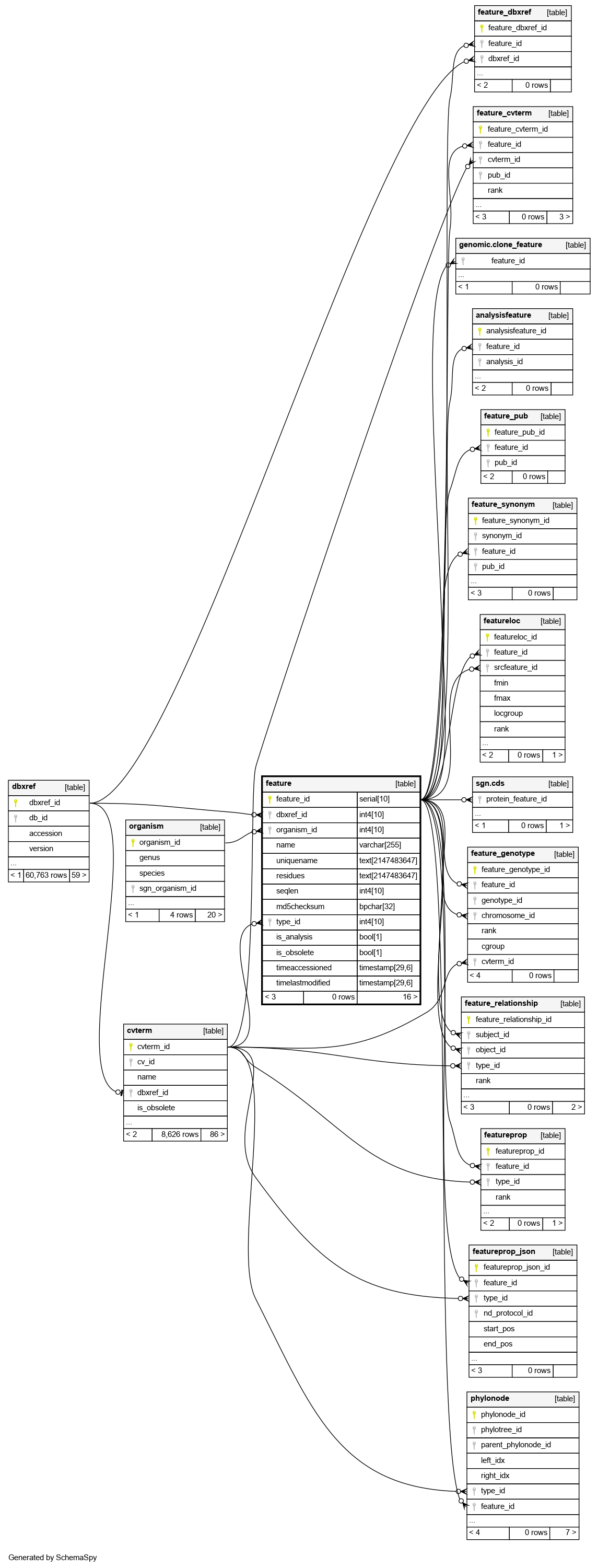
| feature_id | serial | 10 | √ | nextval('feature_feature_id_seq'::regclass) |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| dbxref_id | int4 | 10 | √ | null |
|
|
An optional primary public stable identifier for this feature. Secondary identifiers and external dbxrefs go in table:feature_dbxref |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| organism_id | int4 | 10 | null |
|
|
The organism to which this feature belongs. This column is mandatory |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| name | varchar | 255 | √ | null |
|
|
The optional human-readable common name for a feature, for display purposes |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| uniquename | text | 2147483647 | null |
|
|
The unique name for a feature; may not be necessarily be particularly human-readable, although this is prefered. This name must be unique for this type of feature within this organism |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| residues | text | 2147483647 | √ | null |
|
|
A sequence of alphabetic characters representing biological residues (nucleic acids, amino acids). This column does not need to be manifested for all features; it is optional for features such as exons where the residues can be derived from the featureloc. It is recommended that the value for this column be manifested for features which may may non-contiguous sublocations (eg transcripts), since derivation at query time is non-trivial. For expressed sequence, the DNA sequence should be used rather than the RNA sequence |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| seqlen | int4 | 10 | √ | null |
|
|
The length of the residue feature. See column:residues. This column is partially redundant with the residues column, and also with featureloc. This column is required because the location may be unknown and the residue sequence may not be manifested, yet it may be desirable to store and query the length of the feature. The seqlen should always be manifested where the length of the sequence is known |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| md5checksum | bpchar | 32 | √ | null |
|
|
The 32-character checksum of the sequence, calculated using the MD5 algorithm. This is practically guaranteed to be unique for any feature. This column thus acts as a unique identifier on the mathematical sequence |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| type_id | int4 | 10 | null |
|
|
A required reference to a table:cvterm giving the feature type. This will typically be a Sequence Ontology identifier. This column is thus used to subclass the feature table |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| is_analysis | bool | 1 | false |
|
|
Boolean indicating whether this feature is annotated or the result of an automated analysis. Analysis results also use the companalysis module. Note that the dividing line between analysis/annotation may be fuzzy, this should be determined on a per-project basis in a consistent manner. One requirement is that there should only be one non-analysis version of each wild-type gene feature in a genome, whereas the same gene feature can be predicted multiple times in different analyses |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| is_obsolete | bool | 1 | false |
|
|
Boolean indicating whether this feature has been obsoleted. Some chado instances may choose to simply remove the feature altogether, others may choose to keep an obsolete row in the table |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| timeaccessioned | timestamp | 29,6 | ('now'::text)::timestamp(6) with time zone |
|
|
for handling object accession/modification timestamps (as opposed to db auditing info, handled elsewhere). The expectation is that these fields would be available to software interacting with chado |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| timelastmodified | timestamp | 29,6 | ('now'::text)::timestamp(6) with time zone |
|
|
for handling object accession/modification timestamps (as opposed to db auditing info, handled elsewhere). The expectation is that these fields would be available to software interacting with chado |
Indexes
| Constraint Name | Type | Sort | Column(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| feature_pkey | Primary key | Asc | feature_id |
| feature_c1 | Must be unique | Asc/Asc/Asc | organism_id + uniquename + type_id |
| feature_idx1 | Performance | Asc | dbxref_id |
| feature_idx2 | Performance | Asc | organism_id |
| feature_idx3 | Performance | Asc | type_id |
| feature_idx4 | Performance | Asc | uniquename |
| feature_idx5 | Performance | ||
| feature_idx6 | Performance | ||
| feature_name_ind1 | Performance | Asc | name |