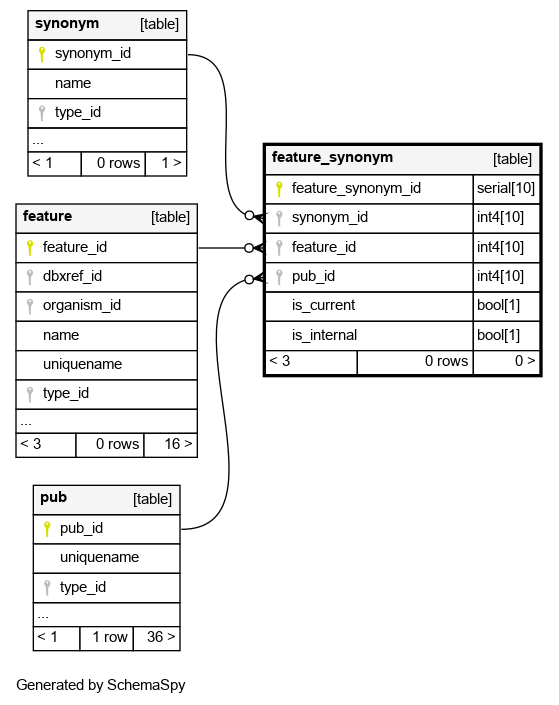
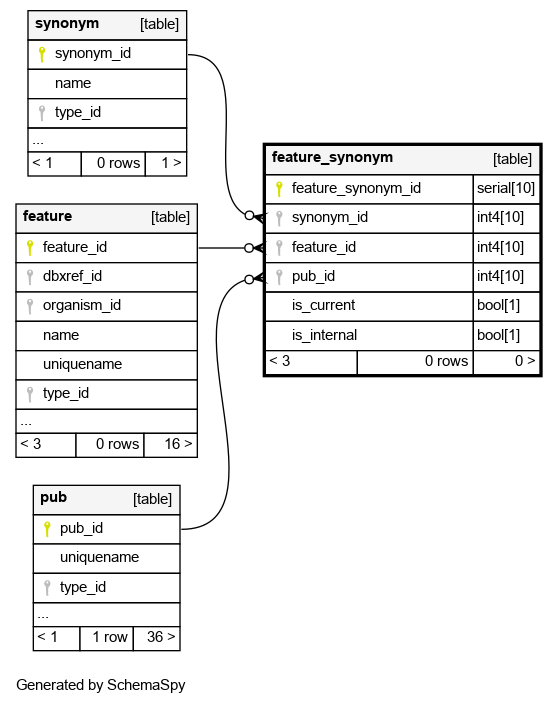
Columns
| Column | Type | Size | Nulls | Auto | Default | Children | Parents | Comments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| feature_synonym_id | serial | 10 | √ | nextval('feature_synonym_feature_synonym_id_seq'::regclass) |
|
|
|||||
| synonym_id | int4 | 10 | null |
|
|
||||||
| feature_id | int4 | 10 | null |
|
|
||||||
| pub_id | int4 | 10 | null |
|
|
the pub_id link is for relating the usage of a given synonym to the publication in which it was used |
|||||
| is_current | bool | 1 | true |
|
|
the is_current boolean indicates whether the linked synonym is the current -official- symbol for the linked feature |
|||||
| is_internal | bool | 1 | false |
|
|
typically a synonym exists so that somebody querying the db with an obsolete name can find the object theyre looking for (under its current name. If the synonym has been used publicly & deliberately (eg in a paper), it my also be listed in reports as a synonym. If the synonym was not used deliberately (eg, there was a typo which went public), then the is_internal boolean may be set to -true- so that it is known that the synonym is -internal- and should be queryable but should not be listed in reports as a valid synonym |
Indexes
| Constraint Name | Type | Sort | Column(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| feature_synonym_pkey | Primary key | Asc | feature_synonym_id |
| feature_synonym_c1 | Must be unique | Asc/Asc/Asc | synonym_id + feature_id + pub_id |
| feature_synonym_idx1 | Performance | Asc | synonym_id |
| feature_synonym_idx2 | Performance | Asc | feature_id |
| feature_synonym_idx3 | Performance | Asc | pub_id |